click on the image to get a detailed view

original in es Juan Pablo Rosas
Durán
es to en Miguel Angel
Sepúlveda
es to en Javier Palacios
Bermejo
Currently system manager for "Optica LUX" in Mexico. He has been
involved with computers since the age of three, when he played with
piles of punched cards in his fathers work and used Gamma10 manuals
as sketch books. His professional experiences with Linux
transformed him completely and since them he tries to apply open
source solutions (with some success) everywhere.
At present he promotes an initiative for the development of GPLed
applications for bussinesses: http://www.pochtecah.org.mx.
He thanks LinuxFocus for the chance to share his Linux experiences
and open source software.
This article dicusses how a medium sized company, focused on the development and production of eye-glasses, has used Linux and open source software to improve its customer support.

Óptica LUX is a company devoted to the development and production of commercial sun and prescription glasses. March 2000 has been the 58th anniversary of this company, and in the last eight years it has doubled its number of retail stores. At present time it has a total of 40 retail stores.
From its beginnings Óptica LUX has promoted a policy of warrantied satisfaction for its customers, and this requires the greatest amount of knowledge of its customer basis, needs and current design preferences.
It is estimated that by the end of 1999, Óptica LUX had information about hundreds of customers. Most of this information, regarding general statistics and optometric data, where recorded in old paper notecards. All this information in its present form is of very limited use.
Our problem consisted in finding a solution to manage this information in order to improve our customer service without introducing any delays in the service provided and its quality. All this should come at no additional cost to the end product.
Before starting it is fundamental to understand the general steps a typical customer of Óptica LUX follows in order to understand the requirements for the application described later on. When a client first arrives at a store:
To our case study of how a typical client is serviced in a retailer store we must add the following considerations in order to put things in context before writing an application:
The above analysis makes it clear that the tool needed to support our customers must be quite unique and specialized.
From 1990 we have studied and tested various propiertary systems specialized for optics retail stores, but none of them really satisfy all of the requirements described above. Adopting any of these commerical solutions would have required to alter significantly the way Óptica LUX interacts with its customers and manages its information, it would have also meant to pay twice as much the software value in order to pay for the modifications required. Proprietary software has the added disadvantage of making us dependent on a third party software provider.
Back in 1995 we considered for the first time to develop an in-house solution custom made for Óptica LUX needs. However when estimating the costs for licensing the platform and tools (SCO Unix and Informix), it turned out equivalent to that of opening a new retailer store! including installation, optometrics equipment and merchandise!!
It was then decided we would try to look for a viable solution that wouldn't require a huge investment in licenses. The platforms that most called our attention were coherent, qnx and Linux.
We attempted to contact coherent, but by then they ceased to exist.
Qnx had an office in Mexico (in the city of Monterrey N.L.). However their responses were limited to simply sending their advertisement brochures.
We learned about Linux thanks to an article entitled ``Linux una propuesta indecorosa'' (Linux, an indecent proposal), written by Fernando Magariños (better known in the mailing groups as ``Mancha de la Calabaza que ladra''). We sent him an email which was replied by Miguel de Icaza himself (I doubt he remembers it now). He gave us his point of view, what reinforced even more our interest towards Linux.
At first, Linux became interesting to us mainly as a ``Royalty free'' platform. However its underlying principles, its dynamism and the spirit of its community became also very important factors.
The technical support we get for Linux through mailing lists is far more effective than its commercial counterparts. Linux is a stable platform which is constantly getting better and it has a wide range of applications available.
Another factor is that information about Linux and free software is much more accessible than their proprietary counterpart, it is then very easy to get self-educated in the usage of Linux or its tools.
At present time Linux is being used in Óptica LUX not only at retail stores, but also at the main executive offices, particularly in the server side to share files and printers and to store data and execute applications developed for other UNIX machines.
We use Linux also to support the basic communications infrastructure in the company, like a PPP server, a web server, email and ftp (our small ``intranet''), and also for the control and fragmentation of the network traffic.
Lately we have started to use Linux as a desktop platform for end users, but this is a story for another time :-).
The first steps are never easy, and the critical one in the case of Óptica LUX was not to convince the executive management of the technical superiority of Linux as a platform, but of making them conscious that the costs associated with developing a new system, specially one highly specialized, are very high and that it is not a very fast process.
We asked 7 companies or groups for submitting proposals for developing a solution based on Linux, but their bids far overpassed the expenses of the proprietary solutions discussed above.
Next we tried to recruit developers to create an in-house system. Unfortunately, there were still very few people really adept for this platform, and the cost of those who are available was well above the average market price, as it is understandable.
Today it is accepted that the development of open source based solutions can be more expensive than proprietary software, but the results are more satisfactory. In any way, the savings in licensing costs can be used to pay for the required development costs of applications.
In the mid 1999 we hired a consulting group to develop a tool to process the data of our clients based on Linux and the GNU software.
The development was taken in a series of incremental steps. A first analysis of the problem gave us:
Based on this first analysis the group developed a first prototype, which was then tested by our expert optometrist. The users provided some interesting feedback that led to modification in the requirements and a second prototype. We followed several cycles of refinement until arriving to a satisfactory product.
The features of the tools used in the development allowed us to speed up the development process, reusing and perfecting the components of the application.
The tools used can be classified in two groups: those used during analysis, design and documentation and those used during the development of the application.
It is difficult to described briefly such a highly specialized and dense tool. The script that creates the database has more than 1000 lines of SQL code, and the application itself about 15,000 lines of PERL. Therefore we will only mention the most relevant features.
The most important feature of this application is the user interface. To facilitate the usability of the interface it was decided to design a very simple and flat interface. The expert optometrists may feel confortable and familiar given his experiences with other optics equipment.
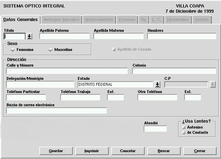
The various elements in the interface are grouped in tabs following the methaphore of a notebook (see following figure). The graphical interface does not require the user to use the mouse to input the data. There are hot keys conveniently located to access every tab in the GUI.
The tabs in the application are as follows:
Hereafter, the most important aspects related to these data groups will be discussed.
The strongest point of this tab is how easy it is to search (and find) data. For example, you can enter a part of the neighborhoud name, select a state from the list, and the application will give you the list of postal codes fulfilling both criteria.

click on the image to get a detailed view
Instead of the neighborhoud, you can enter the district, or both names. In this case a more specific list will be provided by the system.
The postal codes, neighborhoud, district and councils from the whole country are stored in a database with more than 60000 entries. The longest search take no more than 3 seconds to make and display the postal codes list.
These searching facilities are available all along the application. If the user wants to find a person named "Juan", but whose family name could be "Perez" or "Penas", writing "Pe" in the family name box and "Juan" in the name one, after pressing the "Search" button (or the shortcut Ctrl-B) the system will supply a list with every customer fulfilling the criteria.
From everywhere within the application, just pressing Ctrl-A you will get a window with all the customers being attended in this moment, allowing you to identify them with their name and access to any of their data.

click on the image to get a detailed view
This was among the hardest tabs to develop, because it implied major changes in the pTk widget sources, especially for the frame named "Transparent and external medium reviews".
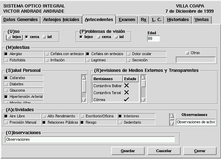
click on the image to get a detailed view
Within that frame the user is able to select any of the available checks, that are shown accompained by a list with all the possible anomalies of each eye.
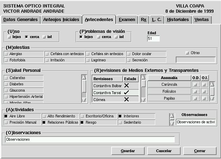
click on the image to get a detailed view
As soon as the optometrist press the "check button", a cross appears close to the label of the selected check. Does anybody know an easy way to do it with VB for example?.
In the Exams tab, a rather complex set of validations are performed. When the optometricist writes down the instruments measurements and decides the correct graduation for the customer, the system checks the correctness of relations among different data and warns the user if there is any condition not fulfilled.
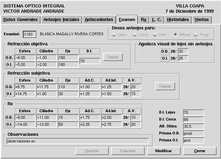
click on the image to get a detailed view
This is the jewel of the application! This piece of code was the one that needed stronger efforts and made arise most of discussion within the development team. Most people using contact lenses can not even imagine the complexity of the amazing thing they wear on their eyes.
Contact lenses are like shoes. In the same way that there are no feets equal all over the world, there is no pair of eyes with the same visual problems.
The application is designed to help the optometrist to select the best type of contact lenses for each customer. It is impossible for the application to decide automatically the correct graduation because there are many non measurable conditions that must be taken into account (for example, those shown in the Optical records tab). However, this module is very useful as a tool to evaluate the impact of many factors over the visual sharpness of each eye.
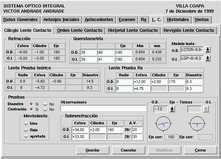
click on the image to get a detailed view
For example, for torus-like contact lenses, the application gives to the optometrist a way to test different corrections for the deviation of the contact lenses axis (lower right corner of the previous figure). As stated before each eyes are unique, and the contact lenses suffer some slight changes to accomodate to the cornea shape, changing the final effective graduation of the eye.
There are other parts of the application that are due to mention because of their unique characteristics. One of them is the mechanism to duplicate databases across internet. We were looking for the secure transmission of data from every Optics to the central data storage located at the executive offices.
This mechanism is implemented using modules available from any CPAN mirror site, and some code written for the database manager PostgreSQL, as shown in the graph below.
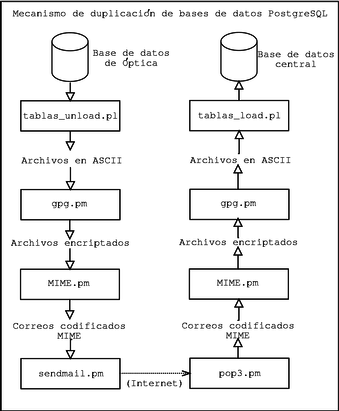
click on the image to get a detailed view
Actually, this development has so many interesting details that we hope to devote a future _LF_ article to it. If the editors give us such a chance :-)
The last point to mention is the use of light computers. As stated in the introduction, one of the requirements was to use computers with the smallest size possible. Due to this, an important task was to study the better choice among second hand 486, slim and ultra-slim boxed computers, and network computers.
The most usable alternatives were:
As the critical point is the physical space we selected network computers with 9'' SVGA screens, because their size (19.05x26.67x3.18 cm) allows them to be placed anywhere within the shop.
The experience with light computers has plenty of interesting details, that we plan to show in a future _LF_ article.
And we could not finish without giving proper recognition to the people that, with their creativity and effort, made it possible that the whole application was Linux based:
Citlali Calderón de Anda: [email protected]
Liliana Araceli Cabello: [email protected]
Juan José Alba
Edgar Raúl Acosta Villaseñor: [email protected]
Gunnar Wolf: [email protected]
Roberto Andrade Fonseca: [email protected]
We believe that some part of the code could be of general interest, as the changes in the pTk widgets, the encripted e-mails sent using perl, and the programs to duplicate and syncronize the PostgreSQL databases, as well as the floppy images for graphical boot disks. Everything will be placed in the future under http://www.pochtecah.org.mx/ABL_GNU.html.