9.3. Module creation, the public part
We continue using the example of Topolino from Section 9.2 and create a very simple module that displays a GIF of Topolino with a list of 3 predefined names that are editable by the users. This is a nonsense module but it's simple enough to be understood by everybody. The DB we will use is MySQL, but the example, by changing some detail, works with all DB's. First of all let's see the skeleton of every module that we will construct:
<?php
if (!eregi("modules.php", $PHP_SELF)) {
die ("You can't access this file directly...");
}
$index = 1;
require_once("mainfile.php");
$module_name = basename(dirname(__FILE__));
get_lang($module_name);
include("header.php");
include("footer.php");
?> |
 | Before making anything it's necessary to create a folder called "modules/Topolino", the file we have just created (with the other contents) must be called index.php and must stay in that folder. |
idperson: It is a cell that contains the id of person (int 11, primary)
nameperson: It is a cell that contains the names of the people (varchar 60)
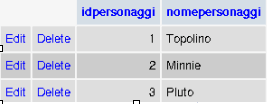
And we manually insert (by using PHPMyAdmin - see Section 11.3 - or an equivalent interface) the names of the 3 people we are interested in, see Figure 9-1 (the module, for simplicity reasons doesn't allow you to add or to cancel people but only editing those that already exist).
Id 1: Topolino
Id 2: Minnie
Id 3: Pluto
 | It's possible to include the footer at the end of every function. It's a solution that is a bit more complex because we must write more lines, but I have to stress how much alot of modules use it. |
 | Attention!!! |
|---|---|
To maintain the abstraction of the DB so that it can work on various database's in an independent way, we cannot use classic PHP syntax that is generally used by the MySQL addicted ; -), instead we must use the syntax illustrated in the file include/sql_layer.php |
The query that we will compile will be structured in the following way:
$resultpersons = sql_query("SELECT idperson, nameperson FROM "$prefix."_topolino", $dbi);
for ($m=0; $m < sql_num_rows($resultpersons, $dbi); $m++)
{
list($idperson, $nameperson) = sql_fetch_row($resultpersons, $dbi);
echo "$idperson - $nameperson < br >";
} |
Very simple, isn't it? OK!, before passing to the administrator's interface for this module, we will start to modify it with the intention of giving it a minimum style dignity.
I would propose:
to insert the results in a table
to put a title to it and a description for the module.
We can do this by rendering all of the module's compatible with the multilanguage system of PHP-Nuke: We define the abstractions that will compose the two phrases we need, in the file lang-english.php we have to insert:
<?php
define("_BENVETOPOMOD", "Topolino Module, Welcome!");
define("_DESCRITOPOMOD", "This is an example module that serves to illustrate how a PHP-Nuke module is created");
> |
Remember to insert a file called index.htm in our language folder! We need it to protect the inside of that folder from undesired navigations. We are nearly at the end of the frontend part, now we have to insert the stylistic part in the code that we have created and to assemble everything. We take two code pieces previously constructed (The initial one and the one created by us) and we join the stylistic modification:
<?php if (!eregi("modules.php", $PHP_SELF))
{ die ("You can't access this rows directly..."); }
$index = 1; require_once("mainfile.php");
$module_name = basename(dirname(__FILE__));
get_lang($module_name);
include("header.php");
echo "<br>";
echo""._BENVETOPOMOD."";
echo "<br><br>";
opentable();
echo "<br>";
echo""._DESCRITOPOMOD."";
echo "<br><br>";
$resultpersons = sql_query("SELECT idperson, nameperson FROM ".$prefix."_topolino", $dbi);
for ($m=0; $m < sql_num_rows($resultpersons, $dbi);
$m++) { list($idperson, $nameperson) = sql_fetch_row($resultpersons, $dbi); echo "$idperson - $nameperson <br>";
}
closetable();
include("footer.php");
?> |
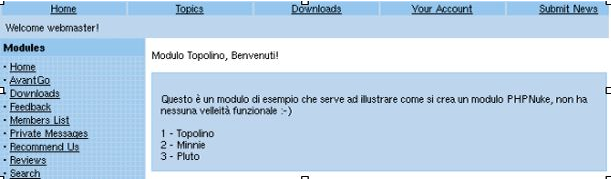
We have only added text, some breaks for the headers and an "Opentable();" and a "Closetable();" to include the text. The result can be seen in Figure 9-2